How to Prevent Periodontitis
Because plaque is constantly forming on your teeth, it is crucial to remove it daily by brushing and flossing. Daily home care partnered with regular dental hygiene appointments are the best way to prevent periodontal disease or its progression.
Treating Periodontal Disease
Treating periodontal disease includes non-surgical and surgical procedures. Treatment methods depend upon the type and severity of the disease.
Non Surgical
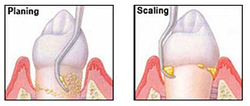
The first non- surgical step usually involves a special cleaning called scaling and root planing. Scaling and root planing is a deep cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar deposits from below the gum line. You will also be given instructions on how to care for your teeth and gums. Once scaling and root planing is completed another appointment will be made about 4 weeks later to re-evaluate the gum pockets and decide if any areas need further treatment.
Non Surgical
The first non- surgical step usually involves a special cleaning called scaling and root planing. Scaling and root planing is a deep cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar deposits from below the gum line. You will also be given instructions on how to care for your teeth and gums. Once scaling and root planing is completed another appointment will be made about 4 weeks later to re-evaluate the gum pockets and decide if any areas need further treatment.
Surgical
Pocket Reduction: This surgery allows the periodontist to access hard-to-reach areas that require removal of tartar and plaque. This procedure will smooth/correct defects and irregularities in the bone surrounding the teeth. Then, the gums are sutured into a new position making the tissue snug around the tooth; therefore, reducing the pocket and making it a maintainable environment.
Crown Lengthening: This procedure involves removal of excess gum and bone tissue to give the general dentist access to the natural tooth for treatment.
Soft Tissue Grafting: Gum grafts are used to cover roots or develop gum tissue where absent due to excessive gingival recession. This can be done for one tooth or several teeth. The tissue used can be taken from your palate or a donated Alloderm source.
Bone Regeneration: This procedure is used to encourage your body’s natural ability to regenerate bone and tissue. The dentist will utilize barrier membranes to direct the growth of new bone at sites having insufficient volumes or dimensions of bone for proper function.
Dental Implants: Dental implants can be used to replace one or more missing teeth. They do not attach to adjacent teeth like a bridge; instead an artificial tooth root is placed by the Periodontist into the jaw and the general dentist places a crown on top. It feels very natural when the procedure is complete. They can also be used to support a denture and make it feel more secure and comfortable. The advantages of replacing a tooth with a dental implant are that it will restore the chewing surface, look esthetically pleasing, be a long-term solution, and maintain the bone in the area that your tooth was lost.
Periodontal cosmetic procedures can improve your smile if you have any of the following concerns: gummy smile/uneven gum line, missing teeth, long teeth/exposed roots, indentation in gums/jawbone.



